Content Grouping in Google Analytics: Why your eCommerce Business needs it
Posted on 10/26/2023
Reviewed by Arnt Eriksen updated at 11/1/2023
Introduction
If you've been googling "content grouping Google Analytics", "content grouping GA4" trying to figure out what it's all about, look no further. In this article, we'll tell you all you need to know.

Google Analytics 4 provides powerful tools to help e-commerce businesses analyze and improve their website performance.
One of these tools is content grouping, which allows businesses to group similar pages or products together and analyze their performance as a whole. With it, you can gain valuable insights into user behavior and make data-driven decisions to enhance their user experience and boost conversions.
By using content grouping in Google Analytics 4, you can better understand your audience and optimize your website to meet their needs, all while improving the profits.
In this article, we will explain what kinds of eCommerce businesses can benefit from content grouping and how it can contribute to their analytics efforts. We will discuss how content grouping can help businesses understand their website performance better.
Why use Content Grouping?
In simple terms, content grouping allows you to take a number of separate pages from your website and gather them in one place in your Google Analytics. This is done by assigning a label to each page or product and grouping them according to this label. For example, an eCommerce business may group all their products in the "shoes" category together, and put all the products in the "clothing" category in a separate group.
Content grouping is useful for eCommerce businesses because it allows them to analyze their website's performance more effectively. Instead of looking at each page or product individually, you can group content likesimilar pages or products together. This provides a more comprehensive view of how users are interacting with the website and can reveal trends or patterns that may not be apparent when analyzing individual pages or products.
The benefits of GA4 content grouping for eCommerce sites are numerous. It allows businesses to:
- Analyze the performance of their products or pages in a more meaningful way.
- Identify trends or patterns in user behavior that may not be apparent when analyzing individual pages or products.
- Make data-driven decisions about how to improve their website's user experience.
- Optimize their website for specific user segments or audiences.
- Compare the performance of different groups against each other and identify areas for improvement.
Overall, content grouping is a powerful tool that can help eCommerce businesses gain a better understanding of their website's performance and make data-driven decisions to improve their user experience and increase conversions.
How Does Content Grouping Benefit Ecommerce Businesses?
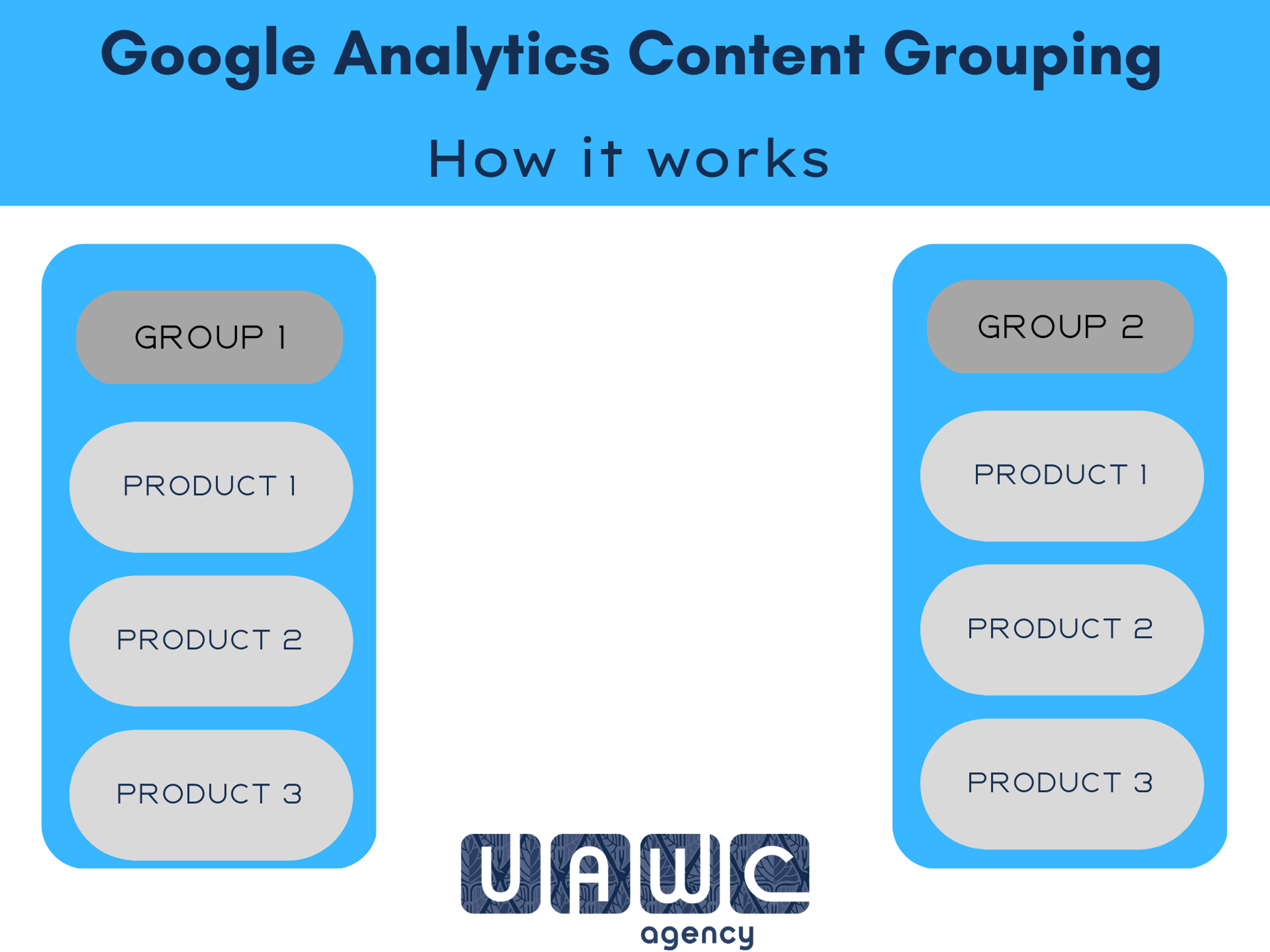
In business, there's no such thing as too much data. Google Analytics gives you enough of it by default. But content grouping can give you more.
Here's how Google Analytics content grouping can benefit eCommerce businesses:
Understanding Website Performance
Content grouping enables eCommerce businesses to analyze their website's performance more effectively. The Google Analytics group pages feature can be used to group pages by content type, user journey stage, or any other relevant dimension. With it, businesses can group similar pages or products together and compare their performance against other groups.
For example, an eCommerce business can group all the products in a particular category and compare the revenue, conversion rate, and other metrics for that category against others. This helps businesses identify which categories are performing well and which ones need improvement.
Making Data-Driven Decisions
By grouping similar pages or products together, eCommerce businesses can get a better understanding of how users are interacting with their websites. You can also visualize this data in Google Data Studio using the "Group by" option.
This can help you make educated decisions about how to improve your website's user experience. For example, if a particular category of product is performing poorly, you can analyze the user behavior, figure out what's wrong, and fix it. You can also identify pages that are causing users to drop off and make improvements to those pages to increase conversions.
Real-World Examples
In our experience, content grouping has benefited many eCommerce businesses in the past. For example, an online clothing retailer we worked with used content grouping to analyze the performance of their product categories. They grouped their products into categories such as men's clothing, women's clothing, and children's clothing. By doing so, they were able to identify which categories were performing well and which ones needed improvement. They discovered that the children's clothing category was performing poorly, and they made changes to improve the category's performance. As a result, the business saw a significant increase in revenue from the children's clothing category.
Another example is a beauty product retailer that used content grouping data to analyze the performance of their product pages. They grouped their product pages by type, such as face products, body products, and hair products. They were able to identify which pages were causing users to drop off and made changes to improve them. As a result, the business saw an increase in conversions and revenue.
How to Set Up Content Grouping in Google Analytics 4 for Ecommerce Sites

Setting up Google Analytics content groupings is an important step for Setting up Google Analytics content groupings is an important step for eCommerce businesses looking to gain more insights into their website performance.
Here is how you can create content grouping in Google Analytics 4:
1. Before you begin, make sure your GA4 is properly set up and running. Do not forget to enable tracking code. See our guide for more instructions on troubleshooting.
2. Define the content groups: Before setting up content grouping, you need to define the groups you want to analyze. This can include categories, product types, or any other meaningful grouping.
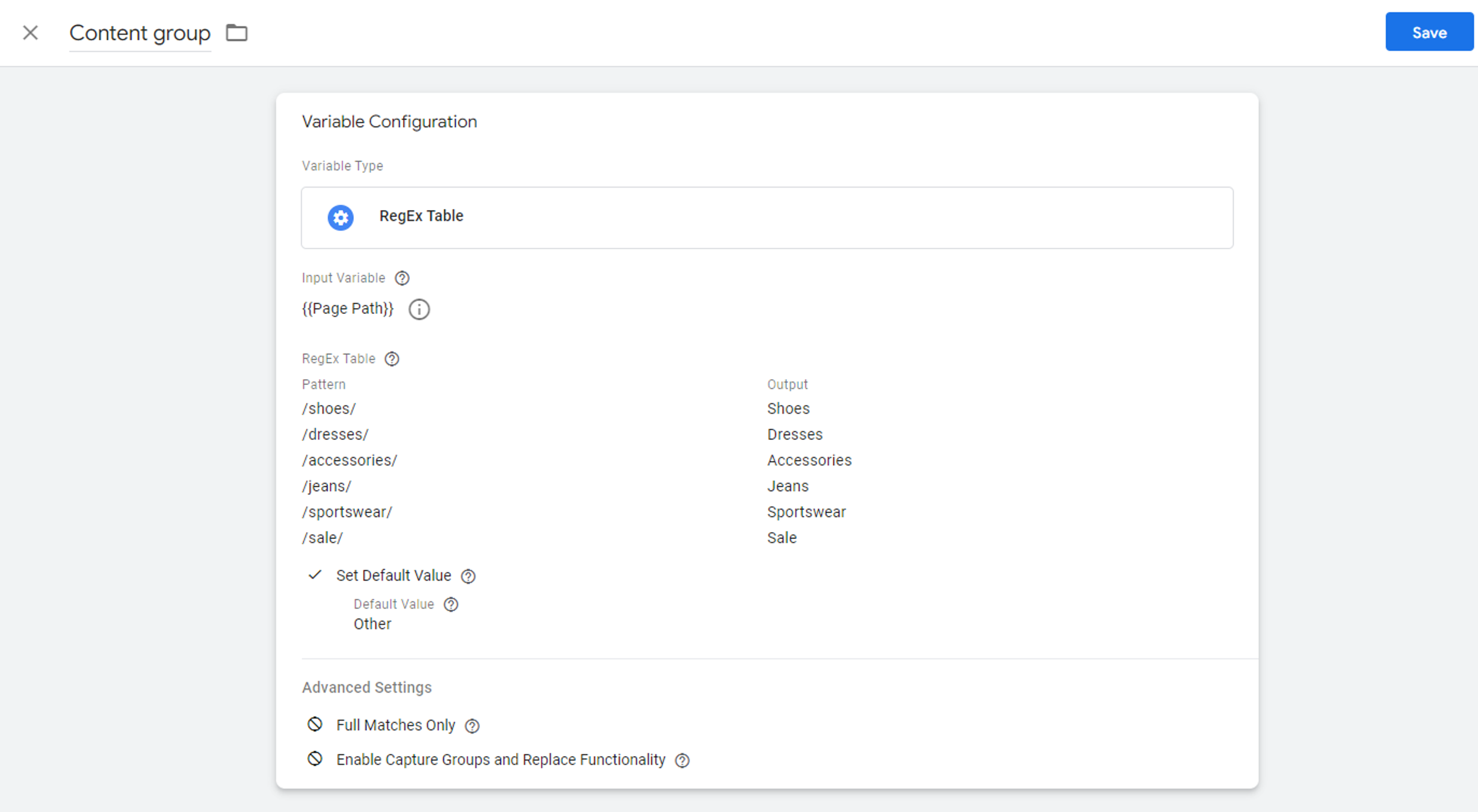
3. Once the groups have been defined, you can implement content grouping for GA4 in Google Tag Manager. For that, you'll need to create a RegEx Table variable and select your Input variable as the rule for the grouping. You can use different variables for this, like Page Title, Page URL, Screen Name, or other.
It will look for the input patterns in the site content, and, in case of a match, provide output values that you want to use to group your content.
Do not forget to specify the Default value when there is no match at all.
Here is a simple example where we have one output for the content group:
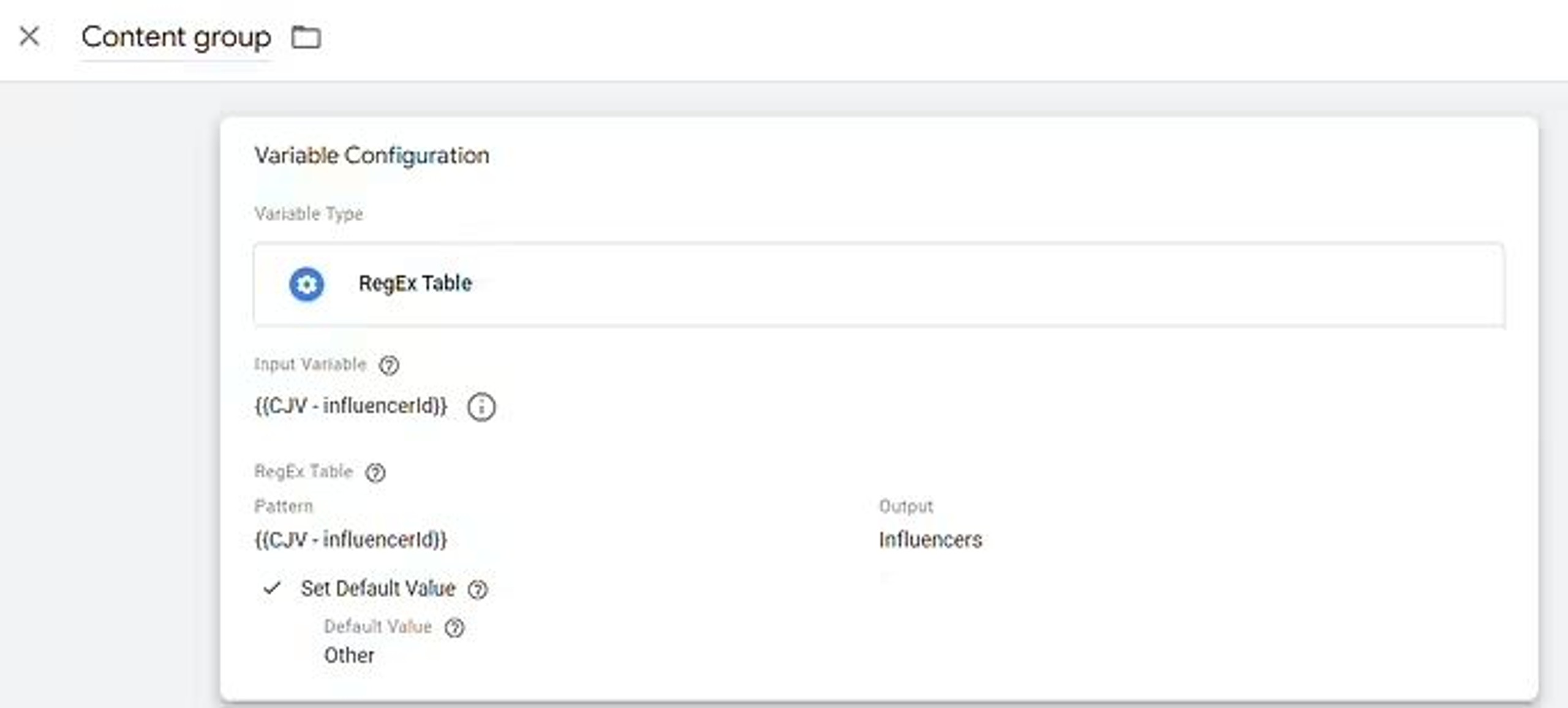
And another example where we have Page path as the Input variable and several output values:
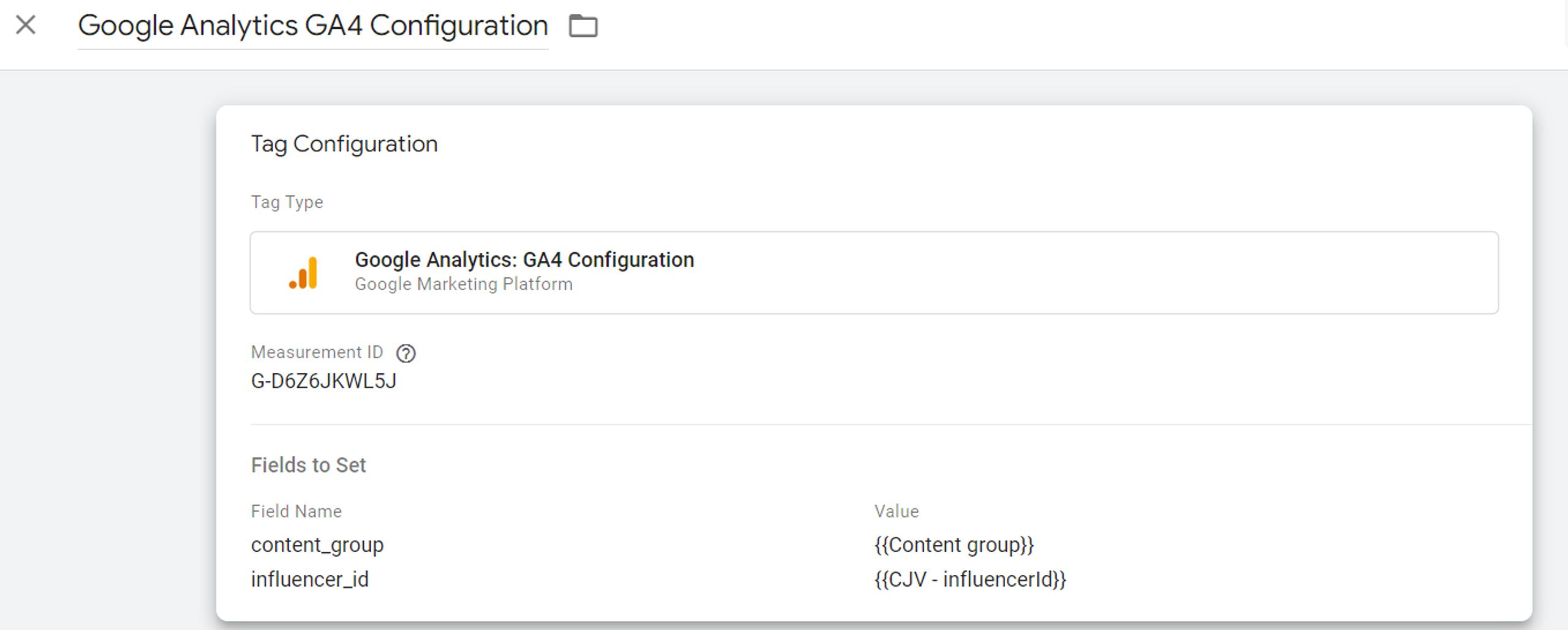
After that, the Content group variable should be added to your GA4 configuration tag as the value for the content_group event parameter:
4. Test the content grouping: After creating the GA4 content group definitions, it's important to test them to ensure they are working correctly.
You can try to open your GTM in Preview mode and you'll find the value of your Content group variable in the list of variables.
Also, open the DebugView section in your GA4 property and there will be the same value for the content_group parameter of the page_view event when debugging:
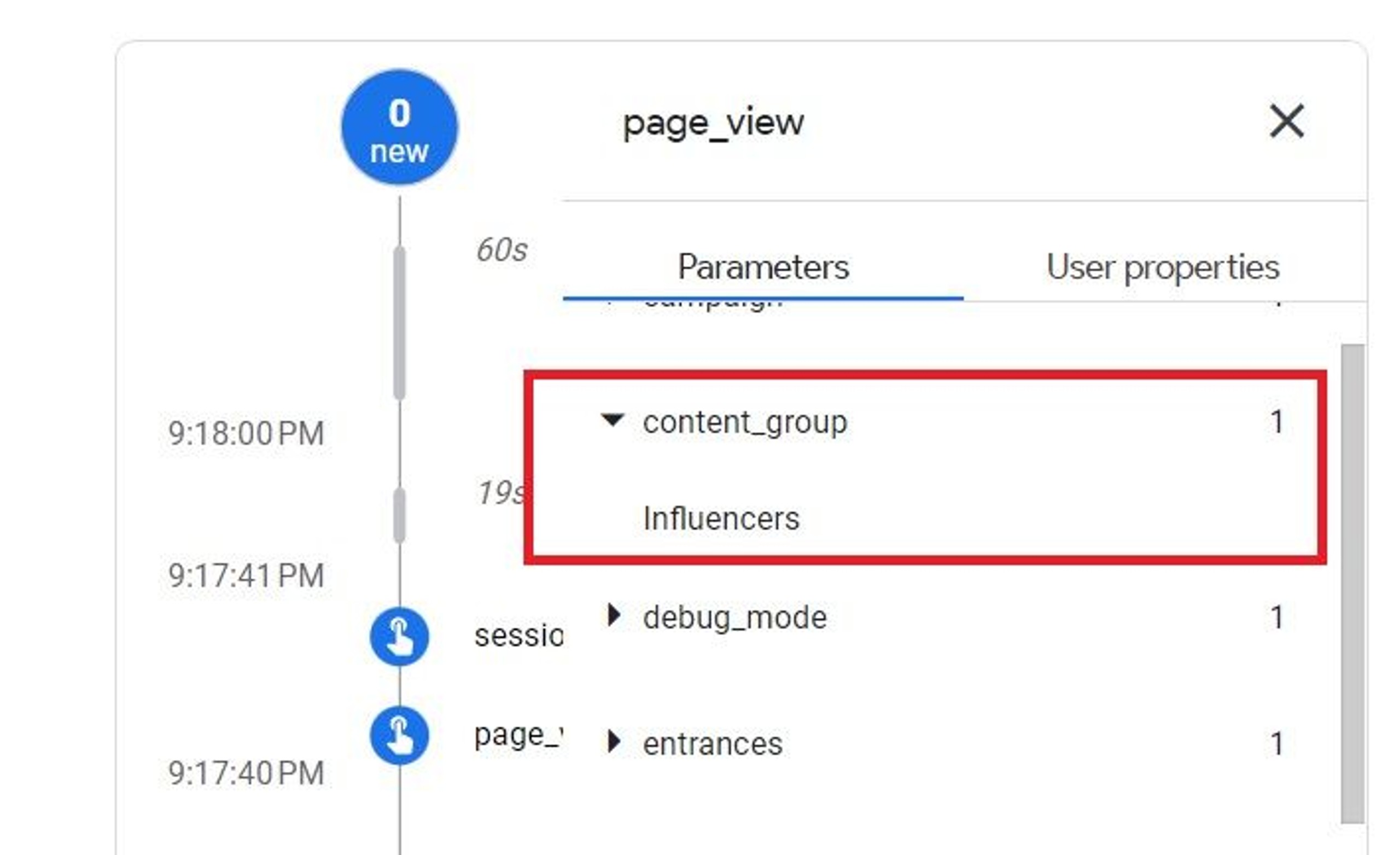
If everything is going well, you can continue by registering your Content group parameter in the Custom definitions section of the GA4 property:
section.
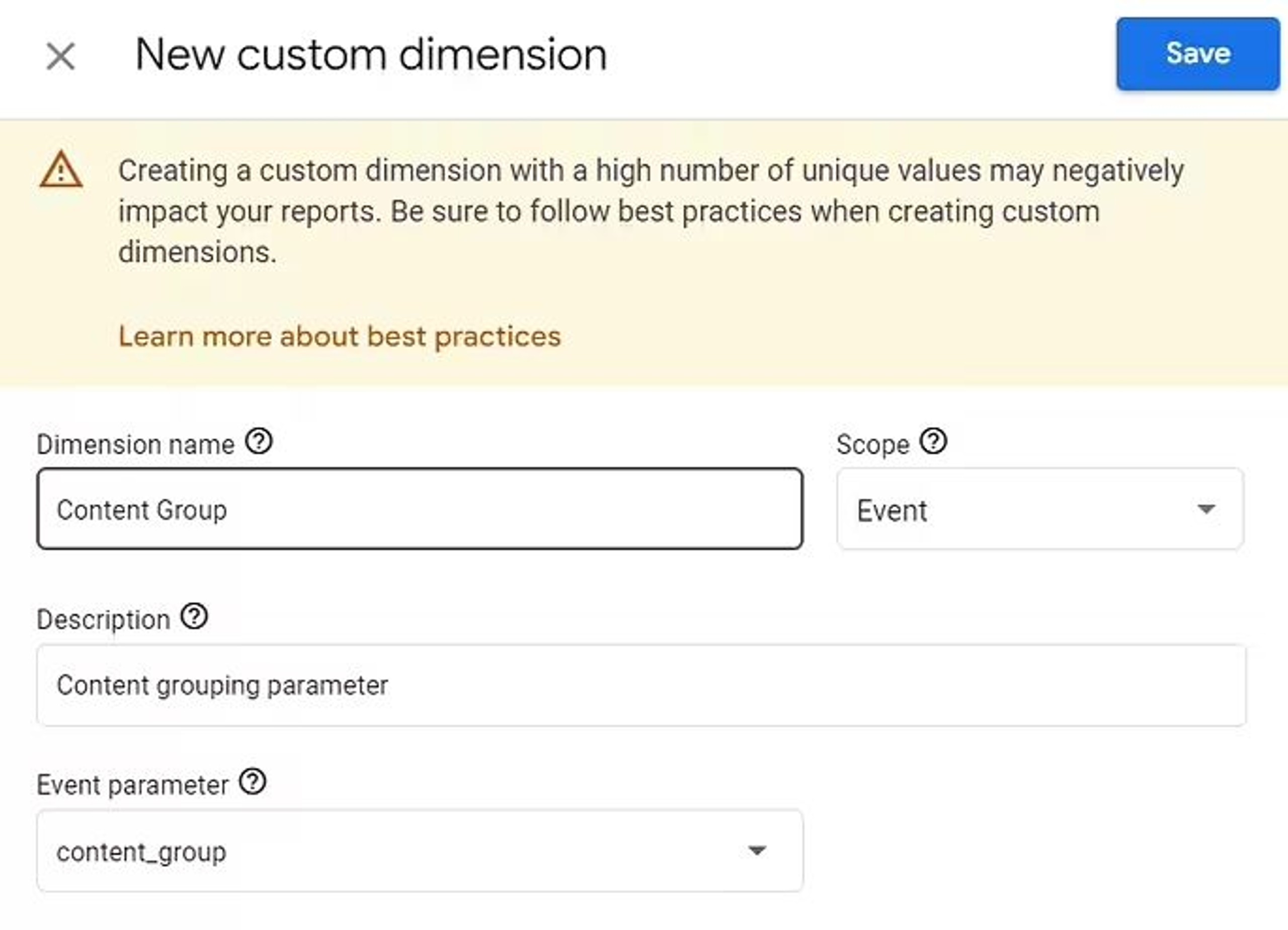
That will give you an opportunity to use this parameter everywhere in your GA4 reports including the Explore section.
5. Analyze the content groups: Once the content grouping has been set up and tested, you can start analyzing the performance of each group.
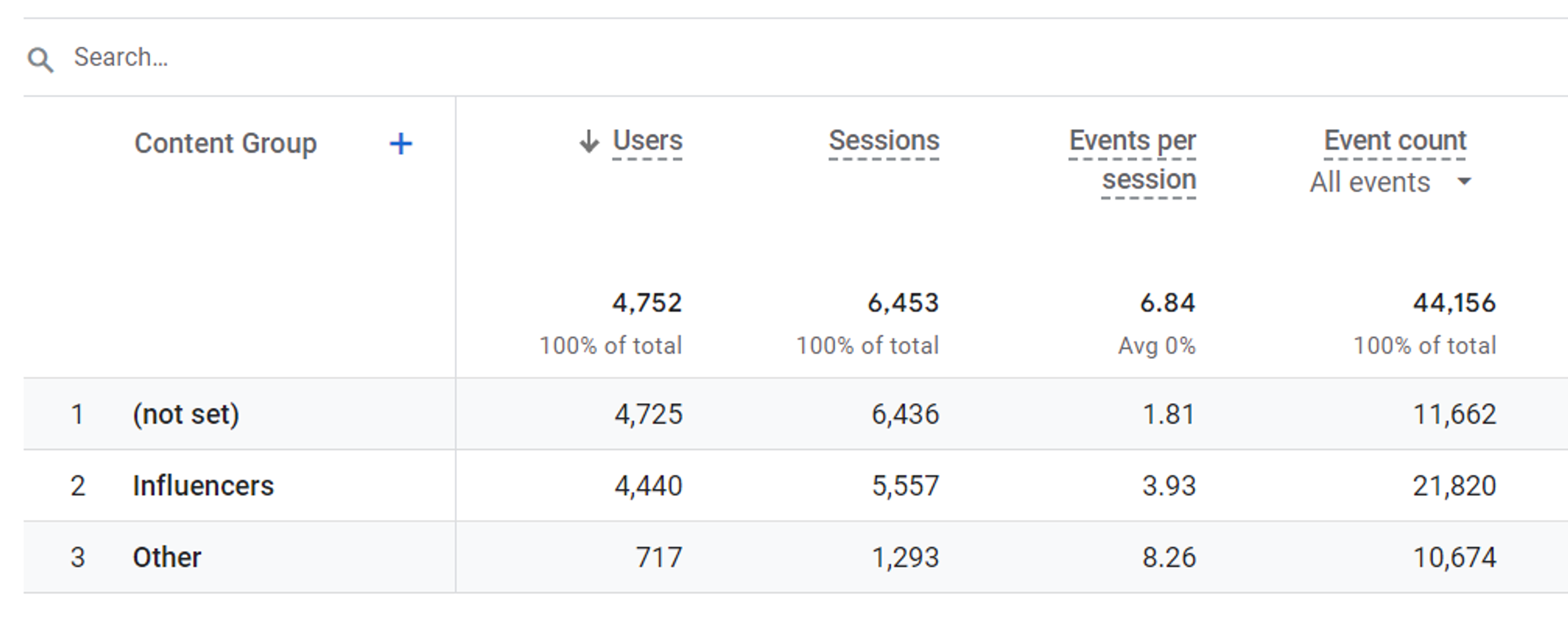
After the setup is finished, you'll be able to use the Content grouping in your reports within 24 hours. You can try to build a standard report:
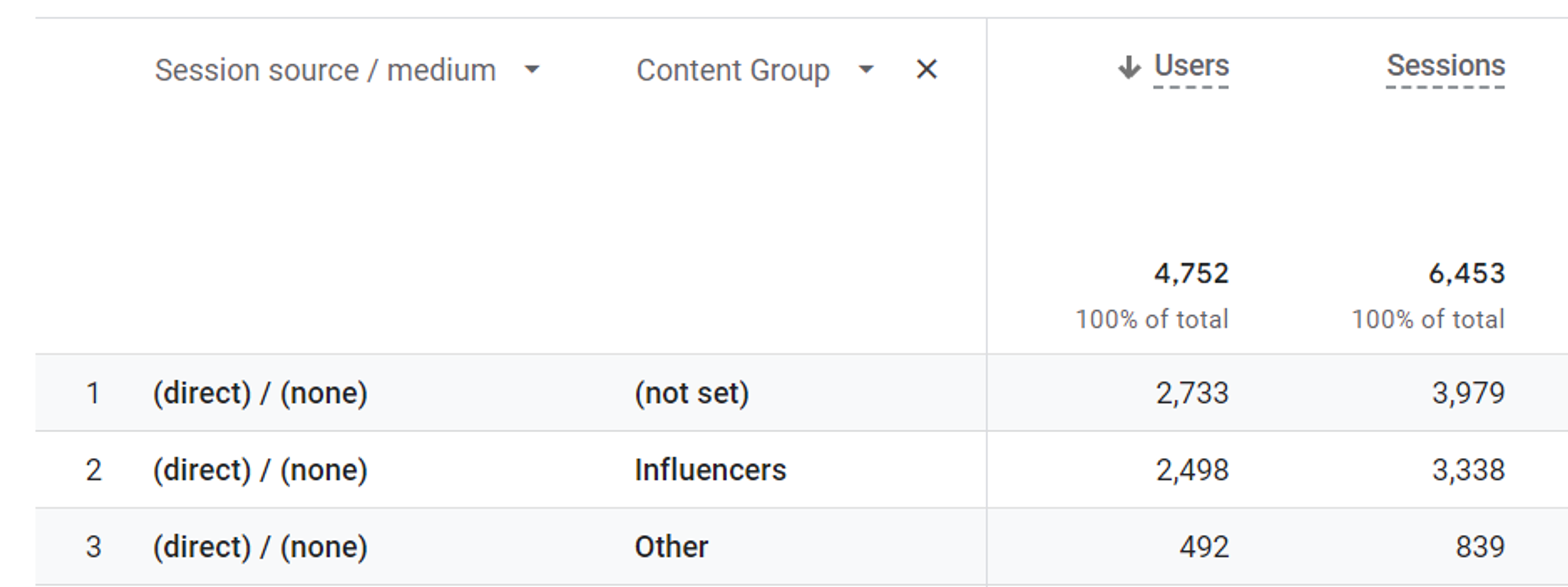
You can use it as a secondary dimension in standard reports:
Or you can even build an audience or a segment using it:
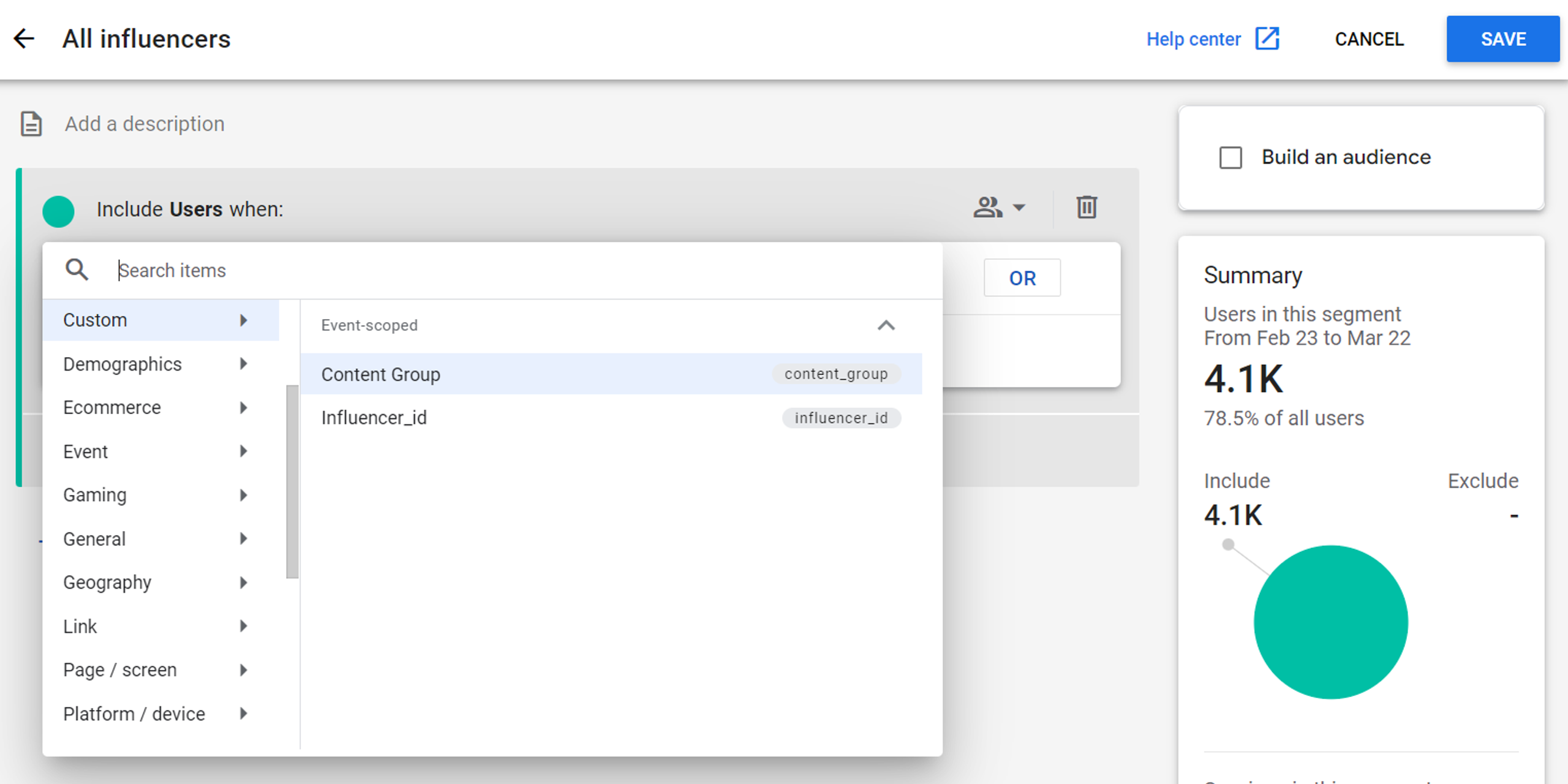
So, it is a really powerful feature when analyzing your data in GA4.
Tips and best practices for content grouping setup include:
- Group pages or products together based on their user journey or behavior.
- Avoid creating too many content groups, as this can make analysis more difficult.
- Regularly review and update content grouping to ensure it remains relevant to your goals and objectives.
- Use custom dimensions to further analyze the performance of content groups, such as comparing the conversion rates of different groups.
Key Metrics to Track with Content Grouping
Once Google Analytics 4 content grouping has been set up, it's important to start tracking key metrics to gain insights into the performance of different groups.
Some key metrics to track with content grouping include:
1. Revenue by product category:
Grouping products together by category allows you to track the revenue generated by each of them. This can help identify which categories are performing well and which may need optimization.
2. Conversion rate by content group:
Tracking the conversion rate of each content group can help identify which groups are driving the most conversions and where optimizations can be made.
3. Average order value by content group:
By tracking the average order value of each content group, you can identify which groups are driving the most revenue per order.
4. Time on page by content group:
Analyzing the time users spend on each content group can provide insights into the effectiveness of the user experience and help identify areas for optimization.
Using these metrics, you can make informed decisions and optimize your site to improve the user experience and increase conversions. For example, if a particular product category has a high conversion rate and average order value, you can focus on promoting and optimizing this category to drive more revenue.
Content grouping can also help identify trends in user behavior. By analyzing metrics over time, you can see if certain content groups are performing better or worse than others and adjust your strategy accordingly. For example, if the time on page for a particular content group is decreasing over time, you may need to investigate why users are spending less time on this group and make optimizations to improve the user experience.
Common Content Grouping Mistakes to Avoid
While content group analytics can be a valuable tool for eCommerce businesses, there are common mistakes that can hinder its effectiveness. Here are some mistakes to avoid when setting up content grouping in Google Analytics 4:
1. Inconsistent naming conventions:
When creating content groups, it's important to use consistent naming conventions to ensure accurate tracking. For example, using different names for the same product category can result in inaccurate reporting.
2. Overcomplicating content groups:
Creating too many content groups or grouping web pages and products that are not related can make it difficult to gain meaningful insights. It's important to focus on grouping similar products and pages.
3. Not utilizing the full potential of content grouping:
Content grouping can be used for more than just product categories. For example, grouping landing pages by customer journey stage or by marketing channel can provide valuable insights into user behavior and the effectiveness of marketing efforts. If you are into content marketing, you can group your blog posts based on authors, topics, length, styles, or other parameters.
4. Not regularly reviewing and updating content groups:
User behavior and website performance can change over time, so it's important to regularly review and update content groups to ensure they are still providing relevant insights.
Limitations of Content Grouping
As useful as content grouping is, it is not perfect. There are certain limitations that you'll need to work around.
One of the main limiting factors of GA4 content grouping is that GA4 content grouping does not support hierarchical grouping. This means that if you want to group your content by nested categories (e.g. "Food > Recipes > Desserts"), you'll need to use a workaround such as creating a custom dimension for each level.
In addition, GA4 content grouping does not currently support retroactive grouping. This means that if you change your content grouping settings, your historical data will not be updated to reflect the new grouping.
It is also worth noting that GA4 content grouping is still a relatively new feature and may not be as robust or customizable as some users would like. However, Google is continually updating and improving GA4, so it's likely that these limitations will be addressed in future updates.
Despite these limitations, GA4 content grouping remains a valuable tool for analyzing and optimizing website performance. By grouping your content based on URL and title, you can gain insights into which pages are most popular and how users are interacting with your website.
Conclusion
Content grouping is a valuable tool for eСommerce businesses to gain insights into website performance and make data-driven decisions.
Setting up content grouping in Google Analytics 4 may seem daunting, but the benefits are worth the effort. By accurately tracking metrics such as revenue by product category and identifying trends in user behavior, eСommerce businesses can optimize their website and increase revenue.
In conclusion, content grouping is an essential tool for eСommerce businesses in Google Analytics 4. By following best practices and avoiding common mistakes, businesses can make the most of content grouping and gain valuable insights into website performance. We encourage eСommerce businesses to set up content grouping for their site and start using it to make informed decisions that will ultimately lead to success.
